Types of Mesothelioma - When people refer to various types of mesothelioma, they usually talk about different places in the body where mesothelioma develops. But things can be a little confusing because there are various types of mesothelioma cells that may appear in each location as well.
These factors affect your prognosis. Your oncologist considers them when making your treatment plan.
Key Facts about Types of Mesothelioma
- Mesothelioma is most likely to develop in the lining around the lungs or stomach
- The most common cell type, epithelioid, is also the most responsive to treatment
- Treatment is tailored to your specific mesothelioma type, to the microscopic cells that make up cancer
- Clinical trials can recruit participants based on their type of mesothelioma
The treatment plan that your doctor recommends will depend largely on the location of your cancer. Your cell type, age, health level and overall cancer will play a role.
There are five known types of mesothelioma. The four listed below are malignant cancers, and benign mesothelioma is a non-cancerous condition.
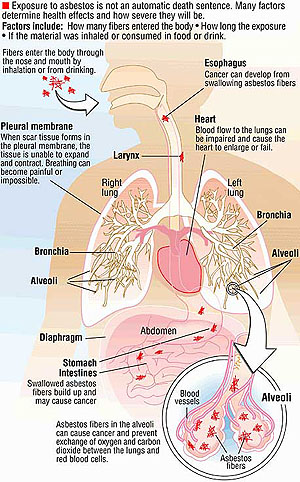
Pleural Mesothelioma: This type of mesothelioma develops in the lining of the lungs, known as the pleura. It is the most common form of malignant mesothelioma, with around 75 percent of cases being pleural in origin.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma: Comprising approximately 20 percent of mesothelioma cases, this form of mesothelioma develops in the lining of the abdominal cavity, known as the peritoneal membrane.
Pericardial Mesothelioma: This form of mesothelioma develops in the lining of the heart, known as the pericardium. Approximately 5 percent of all mesothelioma cases are pericardial.
Testicular Mesothelioma: Testicular mesothelioma develops in the tunica vaginalis of the testicles and is the rarest form of the cancer.
Four Types of Mesothelioma Identified by Location
The type of mesothelioma that you diagnose is named according to the place it developed. For example, when cancer forms in the pleural layer around the lungs, it is called pleural mesothelioma.- Pleural: Lung layer
- Peritoneal: Overlying the stomach
- Pericardial: Heart sac
- Testes: Testicular layer
But, events vary from year to year. A 2015 study looked at the incidence of mesothelioma from 2003 to 2008 and found that 85 percent of cases were pleural and 7 percent peritoneal.
Every type of mesothelioma causes different symptoms. Treatment is tailored to type, and the prognosis also varies.
Pleural Mesothelioma
- Location: Pleural layer
- Symptoms: Shortness of breath, chest pain, fever and fatigue
- Prognosis: 3+ years at stage 1 vs. 12 months at stage 4
Peritoneal Mesothelioma
- Location: stomach lining
- Symptoms: Abdominal pain and swelling, bloating and intestinal changes
- Prognosis: 52 percent live at least five years after surgery with HIPEC
Pericardial Mesothelioma
- Location: Lining of heart
- Symptoms: irregular heartbeat, chest pain, difficulty breathing and coughing
- Prognosis: Usually ranges from six weeks to 15 months
Testicular Mesothelioma
- Location: The shape in the tunica vaginalis, which is the layer that covers the testicles
- Symptoms: Scrotum swelling, painless testicular lumps
- Prognosis: 2 years
Three Types of Mesothelioma Cells
There are three types of cells that make up mesothelioma tumors:- EPITEL
- SARCOMATOID
- BIPHASIC
Pericardial mesothelioma seems to have approximately the same distribution of the three cell types. About two-thirds of cases of testicular mesothelioma involve epitheloid cells. The rest of the testis is biphasic. Only one case of pure sarcomoid cells was reported in the testicular mesothelioma.
Certain subtypes of these cells correlate with various types of mesothelioma. As an example:
- Well-differentiated papillary cells occur most often in stomach mesothelioma. Only a few cases have been reported in people with other types of mesothelioma.
- Small cell mesothelioma is another type of cell that occurs more often in the stomach.
- A little more than half of mesothelioma desiduoid cases occur in the stomach. A little less than half appears in the lining of the lungs
- Cystic and papillary cells occur more frequently in mesothelioma peritoneum.
- Desmoplastic and lymphohistiocytoid is more common in pleural mesothelioma.
Treatment Adjusted to Your Mesothelioma Type.
The type of mesothelioma you diagnose will affect your treatment choices. Different treatments are used depending on the location of your cancer.Operation
Surgery to remove tumors is different for each type of mesothelioma. Extrapleural pneumonectomy and pleurectomy and decortication are used to remove pleural tumors. Peritoneal tumors are removed by peritonectomy. Pericardial tumors are removed by pericardiectomy. Testicular tumors are removed with inguinal orchiectomy.Chemotherapy drugs
Different chemotherapy drugs are used to treat peritoneal and pleural mesothelioma. Cisplatin and pemetrexed are the most effective treatments for pleural mesothelioma. The combination of gemcitabine, pemetrexed, mitomycin and carboplatin is most effective against peritoneal mesothelioma. There are no special chemotherapy regimens that are consistently effective for pericardial or testicular mesothelioma. The last two types of mesotheliomas are so rare that they are not yet available for research.Radiation therapy
A different approach to radiation therapy is used for all types of mesothelioma. In pleural mesothelioma, radiation therapy is used when surgery is an option or when the tumor has invaded the chest wall. Radiation therapy has not been proven successful or very safe for peritoneal mesothelioma. But it has been successfully used to treat pericardial and testicular mesothelioma.Palliative care
A different procedure is used to drain fluid buildup from around the lungs and stomach. The fluid around the lungs is dried with thoracentesis. Paracentesis is used to drain fluid from the stomach.Your cancer cell type affects treatment in ways that are less direct than its location. Instead, oncologists consider your cell type when deciding how aggressively they can treat your cancer.
Patients with epithelium mesothelioma are more often considered for aggressive treatment plans because their cell types respond best. Patients with sarcoma cells are often less considered for aggressive treatment.
Other factors, such as your cancer stage, your age and overall health, play a role where treatment is recommended. Surgery is recommended for early stage patients who are younger and in good health. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy and immunotherapy are available for every patient regardless of stage or age.